Lesson 1 General Introduction of Hypertension
The cardiovascular system allows blood supply to reach all the organs of the body.
कार्डियोवास्कुलर सिस्टम रक्त की आपूर्ति शरीर के सभी अंगों तक करता है।
The blood flows with a force that pushes against the wall of the arteries. That force is called Blood Pressure.
रक्त एक बल के साथ बहता है जो धमनियों की दीवार पर दबाव डालता है। उस बल को रक्तचाप कहते हैं।
heart is a pump which supplies a certain volume of blood to the arteries, later to the arterioles and peripheral capillaries.
हृदय एक पंप है, जो धमनियों को एक निश्चित मात्रा में रक्त की आपूर्ति करता है, बाद में जो छोटी धमनियाँ और परिधीय केशिकाओं में प्रवाहित होता है।
Blood pressure is determined by cardiac output and total peripheral resistance.
रक्तचाप कार्डियक आउटपुट और कुल परिधीय प्रतिरोध द्वारा निर्धारित होता है।
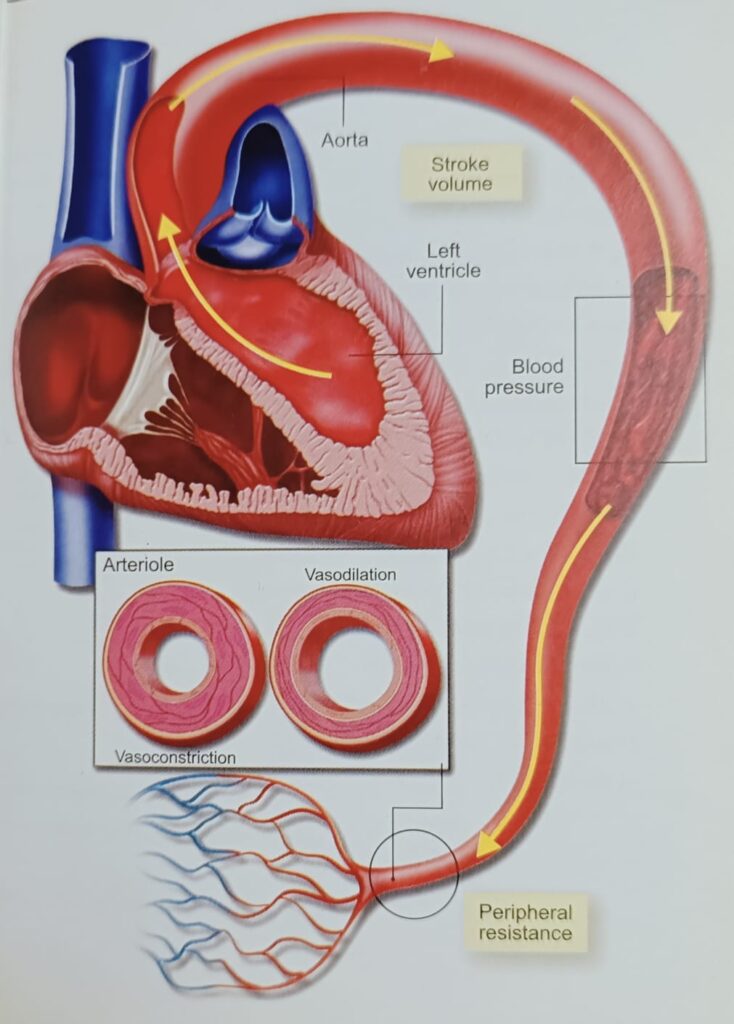
Cardiac output depends on stroke volume and heart rate.
कार्डिएक आउटपुट स्ट्रोक की मात्रा और हृदय गति पर निर्भर करता है।
Peripheral resistance is directly proportional to the length of the arterial system and viscosity, and inversely related to the vessel radius.
परिधीय प्रतिरोध धमनी प्रणाली की लंबाई और चिपचिपाहट के सीधे आनुपातिक है, और रक्त वाहिका की त्रिज्या से विपरीत रूप से संबंधित है।
Peripheral resistance ∝ length of the arterial system and viscosity
∝ 1/fourth power of vessel radius (r⁴)
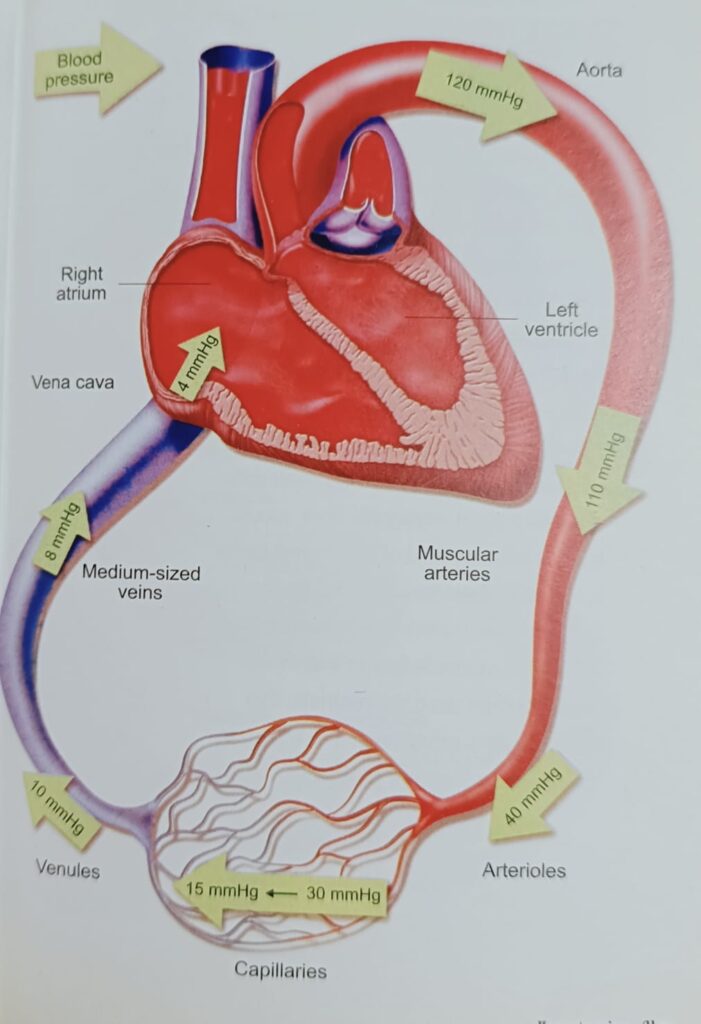
Mean blood pressure falls as blood moves away from the heart.
जैसे ही रक्त हृदय से दूर जाते है, औसत रक्तचाप कम हो जाता है।
The further away from the heart, the lower the pressure.
हृदय से जितना दूर होगा, दबाव उतना ही कम होगा।
According to Darcy’s law, the pressure drop at each region of the vascular system is proportional to the resistance at that section.
डार्सी के नियम के अनुसार, संवहनी तंत्र के प्रत्येक क्षेत्र में दबाव में गिरावट उस खंड पर प्रतिरोध के सामान अनुपात में होता है।
The blood vessels that offer greatest resistance to blood flow are basically arterioles and capillaries, and, to a lesser extent, venules.
रक्त वाहिकाएं जो रक्त प्रवाह के लिए सबसे बड़ा प्रतिरोध प्रदान करती हैं वे मूल रूप से धमनियां और केशिकाएं हैं, और, कुछ हद तक, वेन्यूल्स हैं।
This is due to their vasoconstrictor ability in response to different stimuli.
यह विभिन्न उत्तेजनाओं के जवाब में उनकी वाहिका संकीर्णन की क्षमता के कारण है।
In the systemic circulation, total mean pressure drop is estimated around 100 mmHg.
प्रणालीगत परिसंचरण में, कुल औसत दबाव में कमी लगभग 100 mmHg अनुमानित है।
The lower pressure in the capillary bed facilitates the exchange of gas and nutrients in the tissues.
केशिका जाल में कम दबाव ऊतकों में गैस और पोषक तत्वों के आदान-प्रदान की सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
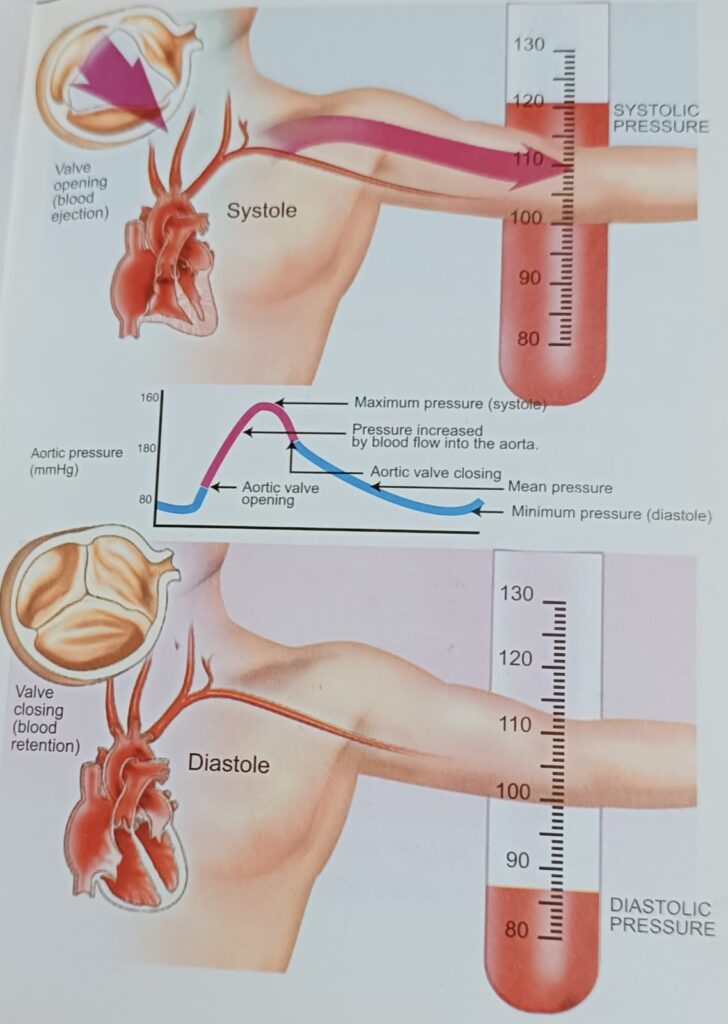
Systolic blood pressure is the highest intravascular pressure reached during systole by ventricular blood ejection; diastolic blood pressure is the intravascular pressure occurring at the end of ventricular diastole, which represents peripheral vascular resistance.
सिस्टोलिक रक्तचाप वेंट्रिकुलर रक्त इजेक्शन द्वारा सिस्टोल के दौरान पहुंचा उच्चतम इंट्रावास्कुलर दबाव है; डायस्टोलिक रक्तचाप वेंट्रिकुलर डायस्टोल के अंत में होने वाला इंट्रावास्कुलर दबाव है, जो परिधीय संवहनी प्रतिरोध का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is known as pulse pressure.
सिस्टोलिक और डायस्टोलिक दबाव के बीच के अंतर को पल्स प्रेशर के रूप में जाना जाता है।
These two pressures determine the so-called mean blood pressure, which consists in the average pressure forcing blood through the arteries towards the body organs; it can be assessed by adding 1/3 of the pulse pressure to the diastolic pressure.
ये दो दबाव तथाकथित औसत रक्तचाप को निर्धारित करते हैं, जिसमें धमनियों के माध्यम से शरीर के अंगों की ओर रक्त को धकेलने वाला औसत दबाव होता है; डायस्टोलिक दबाव में पल्स दबाव का 1/3 जोड़कर इसका आकलन किया जा सकता है।
Mean pressure is especially linked with peripheral resistance, whereas pulse pressure is related to arterial distensibility and wave reflection.
औसत रक्तचाप विशेष रूप से परिधीय प्रतिरोध से जुड़ा होता है, जबकि नाड़ी दबाव धमनी के फूलने की शक्ति और रक्त तरंग से संबंधित होता है।
High blood pressure is a common condition that affects the body’s arteries.
उच्च रक्त दाब एक सामान्य स्थिति है जो शरीर की धमनियों को प्रभावित करती है।
It’s also called hypertension. इसे उच्च रक्तचाप भी कहा जाता है।
In high blood pressure, the force of the blood pushing against the artery walls is consistently too high.
उच्च रक्तचाप में, धमनी की दीवारों पर रक्त का दबाव लगातार बहुत अधिक होता है।
The heart has to work harder to pump blood. रक्त पंप करने के लिए हृदय को अधिक मेहनत करनी पड़ती है।
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
रक्तचाप को पारे के मिलीमीटर (एम एम एचजी) में मापा जाता है।
The usual age of onset is 25-55 years of age. रक्तचाप शुरुआत की सामान्य आयु 25-55 वर्ष है।
A family history of HTN may be present. HTN का पारिवारिक इतिहास मौजूद हो सकता है।
Salt intake in the context of genetic predisposition may be a factor.
आनुवंशिक प्रवृत्ति के संदर्भ में नमक का सेवन एक कारक हो सकता है।
■ Patients with HTN at an early age have primary cause, or new onset >50 y more likely to have secondary HTN cause
कम उम्र में उच्च रक्तचाप वाले मरीजों में प्राथमिक कारण होता है, या नई शुरुआत 50 वर्ष से अधिक होने पर द्वितीयक कारण होने की अधिक संभावना होती है।
Estrogen use (5% of women on estrogen have BP > 140/90; more common in women >35 y, having 5 yrs use, or obese)
एस्ट्रोजेन का उपयोग (एस्ट्रोजन का उपयोग करने वाली 5% महिलाओं का बीपी > 140/90 है; 35 साल से अधिक कि महिलाओं में यह अधिक आम है, जो 5 साल से इसका उपयोग कर रही हैं, या मोटापे से ग्रस्त हैं)
- Normal blood pressure सामान्य रक्तचाप Blood pressure is 120/80 mm of Hg or lower. रक्तचाप 120/80 मिमी एचजी या उससे कम है।
- Elevated blood pressure बढ़ा हुआ रक्तचाप Systolic 120 to 129 mm of Hg and the Diastolic is below, not above, 80 mm of Hg.
सिस्टोलिक 120 से 129 मिमी एचजी और डायस्टोलिक नीचे है, 80 मिमी एचजी से । - Stage 1 hypertension स्टेज 1 उच्च रक्तचाप Systolic 130 to 139 mm of Hg and the Diastolic between 80 and 89 mm of Hg.सिस्टोलिक 130 से 139 मिमी एचजी और डायस्टोलिक 80 और 89 मिमी एचजी के बीच।
- Stage 2 hypertension स्टेज 2 उच्च रक्तचाप Systolic 140 mm of Hg or higher or the Diastolic is 90 mm of Hg or higher. सिस्टोलिक 140 मिमी एचजी या इससे अधिक या डायस्टोलिक 90 मिमी एचजी या इससे अधिक है।
Untreated, high blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and other serious health problems.
अनुपचारित, उच्च रक्तचाप से दिल का दौरा, स्ट्रोक और अन्य गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
It’s important to check your blood pressure at least every two years starting at age 18.
18 साल की उम्र से शुरू करके कम से कम हर दो साल में अपने रक्तचाप की जांच करना महत्वपूर्ण है।
Some people need more-frequent checks.
कुछ लोगों को अधिक बार जांच की आवश्यकता होती है।
Healthy lifestyle habits —such as not smoking, exercising and eating well — can help prevent and treat high blood pressure.
स्वस्थ जीवनशैली की आदतें – जैसे धूम्रपान न करना, व्यायाम करना और अच्छा खाना – उच्च रक्तचाप को रोकने और उसका इलाज करने में मदद कर सकती हैं।
Some people need medicine to treat high blood pressure.
कुछ लोगों को उच्च रक्तचाप के इलाज के लिए दवा की आवश्यकता होती है।
Blood Pressure Regulation रक्तचाप नियमित करने वाले कारक
1. Endothelial cells play a role in the maintenance of vascular tone due to their ability to release chemical mediators.
एंडोथेलियल कोशिकाएं रासायनिक मध्यस्थों को उत्पन्न करने की क्षमता के कारण रक्त वाहिकाओं की मोटाई के नियंत्रण में भूमिका निभाती हैं।
Nitric oxide is a potent vasodilator produced by endothelial cells.
नाइट्रिक ऑक्साइड एंडोथेलियल कोशिकाओं द्वारा निर्मित एक शक्तिशाली रक्त वाहिकाओं का विस्फारक है।
2.Vasodilation leads to decreased peripheral resistance and a drop in blood pressure.
रक्त वाहिकाओं के विस्फारक से परिधीय प्रतिरोध कम हो जाता है और रक्तचाप में गिरावट आती है।
3.Stimulation of the autonomic nervous system can be responsible for both vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
स्वायत्त तंत्रिका तंत्र की उत्तेजना रक्त वाहिकाओं के विस्फारक और रक्त वाहिकाओं के संकुचन दोनों के लिए जिम्मेदार हो सकती है।
4.Baroreceptors are sensory nerve endings which detect wall variations produced by blood pressure changes, and send their stimulus to the nerve centers in the brain.
बैरोरिसेप्टर संवेदी तंत्रिका सिरा होते हैं जो रक्तचाप में परिवर्तन से उत्पन्न दीवार भिन्नताओं का पता लगाते हैं, और मस्तिष्क में तंत्रिका केंद्रों को अपनी उत्तेजना भेजते हैं।
5.Chemoreceptors located in aortic arch and carotid bodies. In presence of severe hypotension, they can be activated by hypoxia, acidosis and hypocapnia.
केमोरिसेप्टर महाधमनी आर्क और कैरोटिड निकायों में स्थित होते हैं। गंभीर हाइपोटेंशन की उपस्थिति में, वे हाइपोक्सिया, एसिडोसिस और हाइपोकेपनिया द्वारा सक्रिय होते हैं।
The main role of chemoreceptors is to increase blood supply to the brain.
कीमो रिसेप्टर्स की मुख्य भूमिका मस्तिष्क में रक्त की आपूर्ति को बढ़ाना है।
6.The antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin is produced by the hypothalamus; promotes urine concentration with sodium reabsorption.
एंटीडाययूरेटिक हार्मोन (एडीएच) या वैसोप्रेसिन हाइपोथैलेमस द्वारा निर्मित होता है; यह सोडियम के पुनः अवशोषण से मूत्र सांद्रता को बढ़ावा देता है।
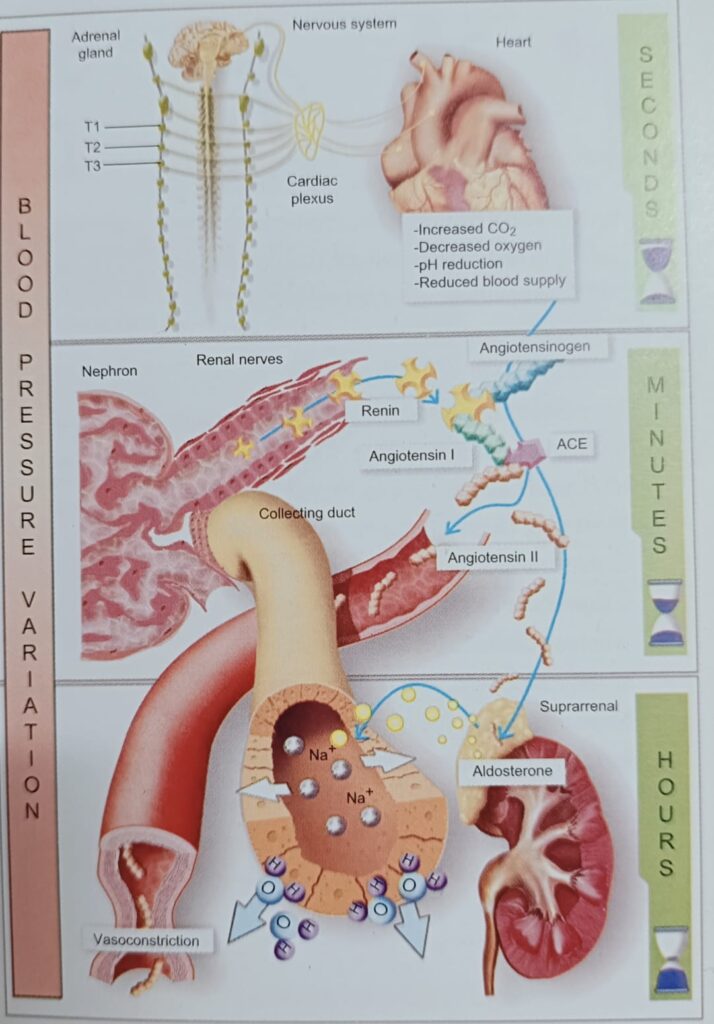
7. The renin-angiotensin hormonal system plays an important role in blood pressure regulation.
रेनिन-एंजियोटेंसिन हार्मोनल प्रणाली रक्तचाप नियमन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती है।
Renin is secreted by the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus, mainly in response to decreased glomerular perfusion.
रेनिन को रीनल जक्सटा ग्लोमेरुलर तंत्र द्वारा स्रावित किया जाता है, मुख्य रूप से ग्लोमेरुलर छिड़काव में कमी के जवाब में।
Renin released converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I (inactive substance) which is, in turn, rapidly converted into angiotensin II, the active substance.
रेनिन स्राव एंजियोटेंसिनोजेन को एंजियोटेंसिन I (निष्क्रिय पदार्थ) में परिवर्तित करता है, जो बदले में, तेजी से एंजियोटेंसिन II, सक्रिय पदार्थ में परिवर्तित हो जाता है।
Being angiotensin II a potent vasoconstrictor, it raises blood pressure.
एंजियोटेंसिन II एक शक्तिशाली वैसोकॉन्स्ट्रिक्टर होने के कारण, यह रक्तचाप बढ़ाता है।
Angiotensin II then promotes aldosterone release by the adrenal cortex; aldosterone acts to retain water and sodium in the kidneys, leading to raised blood pressure due to a volume increase.
एंजियोटेंसिन II तब अधिवृक्क प्रांतस्था द्वारा एल्डोस्टेरोन रिलीज को बढ़ावा देता है; एल्डोस्टेरोन गुर्दे में पानी और सोडियम को बनाए रखने का कार्य करता है, जिससे मात्रा (द्रव की मात्रा) में वृद्धि के कारण रक्तचाप बढ़ जाता है।
Activity related blood pressure changes शारीरिक गतिविधि से संबंधित रक्तचाप में परिवर्तन
Oxygen demand by tissues is increased with physical exercise.
शारीरिक व्यायाम से ऊतकों द्वारा ऑक्सीजन की मांग बढ़ जाती है।
Heart rate rises mainly in response to reduced vagal tone, and a sympathetic stimulus enhances myocardial contractility and promotes blood supply to muscles and skin.
हृदय गति मुख्य रूप से कम वेगस तंत्रिका संबंधी टोन की प्रतिक्रिया में बढ़ जाती है, और एक सिम्पंथेटिक उत्तेजना मायोकार्डियल सिकुड़न को बढ़ाती है और मांसपेशियों और त्वचा में रक्त की आपूर्ति को बढ़ावा देती है।
This vasodilation reduces peripheral resistance, but since cardiac output is increased basically due to the rise in heart rate, blood pressure is maintained or even raised.
यह रक्त वाहिकाओं का विस्फारण परिधीय प्रतिरोध को कम करता है, लेकिन मूल रूप से हृदय गति में वृद्धि के कारण कार्डियक आउटपुट बढ़ जाता है, इसलिए रक्तचाप बना रहता है या बढ़ भी जाता है।
Moderate exercise causes a significant increase in systolic pressure, whereas diastolic pressure undergoes smaller variations, and therefore mean blood pressure is maintained at constant levels.
मध्यम व्यायाम से सिस्टोलिक दबाव में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि होती है, जबकि डायस्टोलिक दबाव में छोटे बदलाव होते हैं, और इसलिए औसत रक्तचाप स्थिर स्तर पर बना रहता है।
More vigorous physical exercise may induce a moderate increase in mean blood pressure.
अधिक ज़ोरदार शारीरिक व्यायाम से औसत रक्तचाप में मध्यम वृद्धि हो सकती है।