Lesson 1: General Introduction of Typhoid
Salmonella typhi bacteria
Typhoid fever is a serious bacterial infection caused by the Salmonella typhi bacteria.टाइफाइड बुखार साल्मोनेला टाइफी बैक्टीरिया के कारण होने वाला एक गंभीर जीवाणु संक्रमण है।
The term typhoid fever was coined because the illness simulated typhus fever ‘like typhus’.टाइफाइड बुखार का नाम ‘टाइफस की तरह’ होने के कारण पड़ा है।
Typhoid fever is also called Enteric fever, because it primarily affects the intestinal tract (आंत्र पथ) and can also spread to the bloodstream, leading to sepsisटाइफाइड बुखार को आंत्र ज्वर भी कहा जाता है क्योंकि यह मुख्य रूप से आँत को प्रभावित करता है और रक्तप्रवाह में भी फैल सकता है, जिससे सेप्सिस हो सकता है ।
It is more prevalent in developing countries, where there are areas with poor sanitation and cleanliness. यह विकासशील देशों में अधिक प्रचलित है, जहां खराब स्वच्छता और साफ-सफाई वाले क्षेत्र हैं।
The infection is spread through contaminated food or water and is more common in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. संक्रमण, दूषित भोजन या पानी से फैलता है, और खराब स्वच्छता और साफ-सफाई वाले क्षेत्रों में आम है।
Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers, which are transmitted by the faecal-oral route, are important causes of fever in India. टाइफाइड और पैराटाइफाइड बुखार, जो मल-मौखिक मार्ग से फैलता है, भारत में बुखार के महत्वपूर्ण कारण हैं।
Symptoms of typhoid fever includes fever, headache, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhoea, and rash. टाइफाइड बुखार के लक्षणों में बुखार, सिरदर्द, पेट में दर्द, कब्ज या दस्त, और दाने हो सकते हैं।
Diagnosis of typhoid fever is typically made through blood culture, stool culture, or serological tests. टाइफाइड बुखार का निदान आम तौर पर ब्लड कल्चर, स्टूल कल्चर या सीरोलॉजिकल टेस्ट के माध्यम से किया जाता है।
The infection can be treated with antibiotics, but some strains of the bacteria have developed resistance to common antibiotics. संक्रमण का एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं के साथ इलाज किया जाता है, लेकिन बैक्टीरिया के कुछ उपभेदों ने सामान्य एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं से प्रतिरोध का विकास कर लिया है ।
Vaccines are also available to prevent this disease. इस रोग से बचाव के लिए वैक्सीन भी उपलब्ध हैं।
It can be severe if left untreated and can lead to serious complications, such as sepsis and perforation of the intestine. यदि बिना इलाज के छोड़ दिया जाए तो यह गंभीर हो सकता है और गंभीर जटिलताओं को जन्म दे सकता है, जैसे कि सेप्सिस और आंत का फटना।
It is important for individuals travelling to areas with high rates of typhoid fever to take precautions to prevent infection, such as avoiding contaminated food and water and getting vaccinated.
टाइफाइड बुखार की उच्च दर वाले क्षेत्रों की यात्रा करने वाले व्यक्तियों के लिए यह महत्वपूर्ण है कि वे संक्रमण को रोकने के लिए सावधानी बरतें, जैसे दूषित भोजन और पानी से बचना और बचाव के लिए वैक्सीन लगवाना।
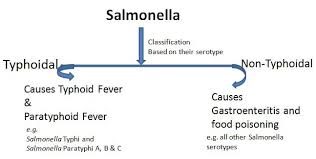
Enteric fevers are caused by infection with Salmonella Typhi and S. paratyphi A and B. टाइफाइड बुखार साल्मोनेला टाइफी और साल्मोनेला पैराटाइफी ए और बी के संक्रमण के कारण होता है।
Salmonellae are a complex group of facultatively anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli that consist of over 2000 serotypes. साल्मोनेला एक अवायवीय (जिसे ऑक्सीजन की ज़रूरत न हो) ग्राम-निगेटिव बैक्टीरिया का एक जटिल समूह है जिसमें 2000 से अधिक सीरोटाइप होते हैं।
Ubiquitous ( देशव्यापी ) in nature, found primarily in the gastrointestinal tracts of wild and domestic animals; exceptions are S. typhi and S. paratyphi, which only colonize humans. सर्वव्यापी (देशव्यापी) प्रकृति का, मुख्य रूप से जंगली और घरेलू जानवरों के पेट तथा आंत संबंधी मार्ग में पाया जाता है,जबकि एस. टाइफी और एस. पैराटाइफी, जो केवल मनुष्यों में पाये जाते हैं।
An acid medium with a pH level of 1.5 or less kills most of the bacilli in our stomach. 1.5 या उससे कम पीएच स्तर वाला अम्लीय माध्यम हमारे पेट में अधिकांश बैक्टीरिया को मारता है।
HIGH-RISK PATIENTS उच्च जोखिम वाले रोगी
Individuals with frequent use of Antacids एंटासिड के लगातार उपयोग करने वाले व्यक्ति
( एंटासिड वे पदार्थ हैं जो आमाशय की अम्लता को उदासीन (न्यूट्रलाइज) करने का काम करते हैं जिससे आमाशय की जलन, अपच आदि से छुटकारा मिलता है),
H2 blockers (Famotidine, Ranitidine)
H2 ब्लॉकर्स (फैमोटिडाइन, रैनिटिडीन)
or या
on proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Esomeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole), जो प्रोटॉन पंप अवरोधकों पर है (ओमेप्राज़ोल, एसोमेप्राज़ोल, लैंसोप्राज़ोल, रबेप्राज़ोल, पैंटोप्राज़ोल),
or या
advanced age with achlorhydria बढ़तीआयु के साथ अम्ल का अभाव,
and post-gastrectomy status और गैस्ट्रेक्टोमी के बाद की स्थिति, यह एक सर्जरी है जिसके जरिए, पेट के कुछ हिस्से या पूरे हिस्से को हटाया जाता है
Humans become infected by eating contaminated food like Ice cream, Eggs, poultry, meat & other dairy products or by direct contact. दूषित भोजन जैसे आइसक्रीम, अंडे, पोल्ट्री, मांस और अन्य डेयरी उत्पाद खाने या सीधे संपर्क से मनुष्य संक्रमित हो जाते हैं।
Serotypes commonly causing human disease are S. typhi, S. paratyphi, S. enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, S. Heidelberg and S. choleraesuis. आमतौर पर मानव में रोग पैदा करने वाले सेरोटाइप एस. टाइफी, एस. पैराटीफी, एस. एंटरिटिडिस, एस. टायफिम्यूरियम, एस. हीडलबर्ग और एस. कोलेरेसुइस हैं।
Classification
Kingdom: Bacteria
Class: Gamma proteobacteria
Genus: Salmonella
Species: Salmonella Typhi
Suspect typhoid when fever is high, continuous, lasting for over a week. The patient looks ill, with mild splenomegaly, Relative bradycardia, Leucopenia and Widal test is positive. टाइफाइड का संदेह तब होता है जब बुखार तेज, लगातार, एक सप्ताह से अधिक समय तक रहता है। रोगी बीमार दिखे,प्लीहा तथा जिगर का बढ़ जाना, सापेक्ष ब्रैडीकार्डिया, ल्यूकोपेनिया और विडाल परीक्षण सकारात्मक है।
Relative bradycardia (सापेक्ष ब्रैडीकार्डिया) as a characteristic feature of typhoid fever means a clinical sign whereby the pulse rate is lower than expected for a given body temperature. टाइफाइड बुखार की एक विशेषता के रूप में सापेक्ष मंदनाड़ी अर्थात नाड़ी की दर किसी दिए गए शरीर के तापमान के लिए अपेक्षा से कम होती है।
Leukopenia (WBC count in enteric or typhoid fever is often low) is thought to be a characteristic finding in patients with typhoid fever. ल्यूकोपेनिया (टाइफाइड बुखार में डब्ल्यूबीसी की संख्या अक्सर कम होती है) को टाइफाइड बुखार के रोगियों में एक विशिष्ट खोज माना जाता है।
After a few days of bacteremia, the bacilli penetrates the mucosa of both small and large intestine and proliferates intracellularly. रोगी के शरीर में बैक्टीरिया के प्रवेश के कुछ दिनों बाद, बैक्टीरिया छोटी और बड़ी आंत दोनों के म्यूकोसा में प्रवेश करता है और इंट्रासेल्युलर रूप से फैलता है।
Bacteria invade and replicate in macrophages of the small intestine, resulting in typical lesions in the Peyer’s patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, Liver and spleen. बैक्टीरिया छोटी आंत के मैक्रोफेज में आक्रमण करते हैं और दोहराते हैं, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप पीयर पैच, मेसेन्टेरिक लिम्फ नोड्स, लिवर और प्लीहा में विशिष्ट घाव हो जाते हैं।
Huckstep’s Four Phases in the evolution of pathology of enteric fever.
एंटरिक फीवर कि पैथोलॉजी के विकास में हॉकस्टेप के चार चरण।
1. Hyperplasia of lymphoid follicles. लिम्फोइड रोम में हाइपरप्लासिया।
2. Necrosis of the lymphoid follicles in the 2nd week involving both mucosa & submucosa.
दूसरे सप्ताह में लिम्फोइड फॉलिकल्स का नेक्रोसिस जिसमें म्यूकोसा और सबम्यूकोसा दोनों शामिल हैं।
3. Ulceration in the long axis of the bowl with the possibility of perforation and haemorrhages.
आंत का फटना और रक्तस्राव की संभावना के साथ आंत की लंबी धुरी में अल्सरेशन।
4. Healing takes place from the 4th week onwards
(long axis ulcer on healing does not result in stricture in contrast to tuberculous transverse axis ulcer which on healing causes stricture).
चौथे सप्ताह के बाद घाव भरना शुरू होता है (लंबे अक्षीय अल्सर घाव, भरने पर सख्त नहीं होता है )।
They swell at first, then ulcerate and usually heal. ये पहले सूज जाते हैं, फिर अल्सर हो जाते हैं और आमतौर पर ठीक हो जाते हैं।
Carriers (वाहक)
Man is the only known reservoir of infection. मनुष्य इस संक्रमण का एकमात्र ज्ञात वाहक है।
The individual is infectious as long as one excretes the bacilli (कीटाणु) in the stool or urine. व्यक्ति तब तक रोग फैलानेवाला रहता है जब तक वह मल या मूत्र में कीटाणुओ को बाहर निकालता रहता है।
Temporary carriers:- This carrier state lasts for less than 6 weeks. अस्थायी वाहक:- यह वाहक अवस्था 6 सप्ताह से कम समय तक रहती है।।
Convalescent carriers :-who have recovered from their illness but remain capable of transmitting disease to others.
आरोग्य वाहक:- जो अपनी बीमारी से ठीक हो गए हैं लेकिन दूसरों को रोग प्रसारित करने में सक्षम हैं।
Incubating carriers :- Those who can transmit bacteria during the incubation period before clinical illness begins.
इनक्यूबेटिंग कैरियर्स:- जो क्लिनिकल बीमारी शुरू होने से पहले कि अवधि के दौरान बैक्टीरिया को प्रसारित कर सकते हैं।
Carriers usually excrete (बहार निकलना) the bacteria for 6 to 8 weeks. वाहक आमतौर पर 6 से 8 सप्ताह तक बैक्टीरिया का उत्सर्जन कर सकते हैं।
After clinical recovery, about 5% of patients become chronic carriers (जो वाहक 1 वर्ष के बाद बैक्टीरिया का बहार निकलना जारी रखें); the bacilli may live in the gallbladder ( पित्ताशय की थैली ) for months or years and pass intermittently ( रुक रुक कर ) in the stool and, commonly, in the urine.
क्लिनिकल रिकवरी के बाद, लगभग 5% रोगी क्रोनिक कैरियर्स बन जाते हैं ,बैक्टीरिया पित्ताशय की थैली में महीनों या वर्षों तक रह सकता है और रुक-रुक कर मल में और आमतौर पर मूत्र में निकल सकता है।